Is the future of commerce already here, hidden in plain sight? The subscription model, once a niche concept, is rapidly transforming the global economy, promising a world where access often trumps ownership and recurring revenue reigns supreme.
The subscription business model, a concept that has evolved since the seventeenth century, has undeniably captured the imagination and wallets of consumers and businesses alike. The remarkable surge in popularity, however, isn't just a fleeting trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how we consume goods and services. This shift, fueled by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences, is reshaping industries and opening up new avenues for growth and innovation. This article delves deep into the mechanics of subscription models, explores their diverse applications across various sectors, and examines the reasons behind their remarkable traction. Moreover, it offers insights into the advantages for both businesses and consumers in this ever-evolving landscape.
Let's examine the core characteristics of subscription models and how they're changing the economic landscape.
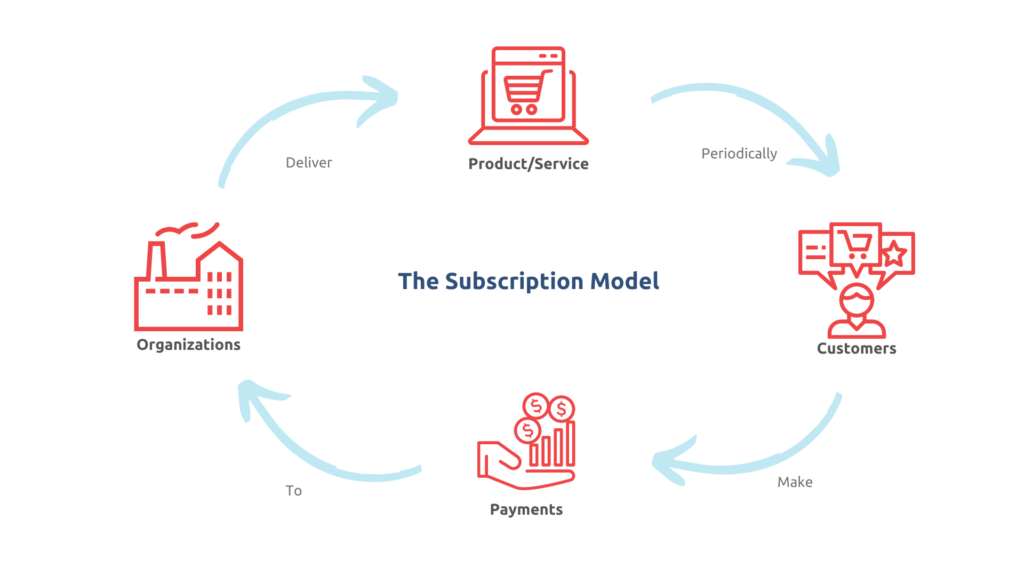
The Subscription Model
At the heart of the subscription model lies a simple yet powerful concept: regular payments in exchange for ongoing access to a product or service. Customers pay repeatedly at set intervals, whether monthly, annually, or based on usage. This recurring revenue stream is a key differentiator from traditional transaction-based business models and offers significant advantages for both providers and consumers.
From a business perspective, subscription models offer predictability and stability. They provide a steady income stream, allowing companies to forecast revenue more accurately and invest in long-term growth initiatives. This predictability can be especially crucial in volatile economic environments. Further, subscription models facilitate strong customer relationships, fostering loyalty and providing opportunities for continuous engagement. Businesses can collect valuable data about customer behavior and preferences, enabling them to tailor their offerings, personalize the user experience, and drive customer lifetime value (LTV). This data-driven approach allows for iterative improvements, ensuring the product or service remains relevant and valuable over time.
For consumers, subscription models offer convenience, flexibility, and often, cost savings. They provide access to a wide range of products and services on demand, eliminating the need for upfront investments or long-term commitments. Furthermore, subscription services frequently include added value such as exclusive content, premium features, or personalized support, which can enhance the overall user experience. The emphasis on continuous improvement also benefits consumers; the supplier is incentivized to upgrade their product to retain subscribers.
The appeal of subscription models spans a vast spectrum of industries. The growth of SaaS subscription model in particular is something to explore more in detail. Software as a Service (SaaS) is where customers continuously use the software and it is often updated, and companies such as Google Workspace, Hubspot, Adobe, and Slack all have subscription models, meaning that the user has to pay recurring revenue to avail of their services.
The Rise of Subscriptions
The increasing popularity of subscription models can be attributed to several converging factors. Firstly, technological advancements have lowered the barriers to entry for businesses, enabling them to develop and deliver subscription-based services more easily. Cloud computing, sophisticated payment processing systems, and data analytics tools have all played a role in making subscription models more accessible and scalable. In addition, the proliferation of mobile devices and the increasing prevalence of high-speed internet have created a more connected and on-demand society. Consumers are now accustomed to accessing content and services anytime, anywhere, which perfectly aligns with the subscription model's convenience and flexibility.
Secondly, evolving consumer preferences are driving the adoption of subscriptions. Consumers are increasingly valuing access over ownership, preferring to pay for the utility of a product or service rather than owning it outright. This shift is particularly evident among younger generations who prioritize experiences and convenience. The rise of the sharing economy and the growing popularity of experiences over possessions further reinforce this trend. The convenience factor plays a significant role. Customers get the convenience of automatically having the product when they need it, or getting immediate access to new features. Businesses get a more stable source of income.
Thirdly, subscription models offer a unique value proposition that aligns with evolving consumer demands and technological advancements. Whether accessing curated content or leveraging business tools, these models provide a clear path to value. This focus on value also extends to sustainability. Subscription services often promote the efficient use of resources and minimize waste. Consider streaming services that reduce the need for physical media or software subscriptions that eliminate the need to purchase and maintain physical copies. The global subscription economy market size is projected to be $1.5 trillion in 2025, up from $650 billion in 2020, highlighting the rapid expansion of this sector.
An average US consumer spent $273 monthly on subscription services in 2021. This significant boost in LTV underscores the potential for sustainable growth and profitability. McKinsey & Company estimates the global subscription industry will reach $2 trillion by 2025. This astronomical number isn't surprising, since 86% of Americans pay for at least one subscription service. This trend in subscription services and usage shows no signs of slowing.
Subscription models offer the business several advantages, including a reliable income stream, stronger customer relationships, and improved customer loyalty. These models allow companies to predict revenue, foster closer relationships with customers, and create opportunities to personalize products and services. The potential for sustainable growth and profitability is also enhanced.
But what are the types of subscription models?
Types of Subscription Models
Subscription businesses can be classified into B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) models, depending on their target audience. Within these categories, a variety of subscription models exist.
Some popular subscription business models include:
Software as a Service (SaaS): Customers pay for continuous access to software that is often updated. Google Workspace, HubSpot, Adobe, and Slack are prime examples. The SaaS subscription model is particularly popular because it allows businesses to get the most out of their digital resources, while continuously improving their software offerings.
Content Subscriptions: Media outlets, streaming services, and educational platforms use this model to provide access to premium content, such as news articles, videos, music, and courses. These models often involve a recurring payment for access to a curated selection of content, with frequent updates and new releases. Netflix and Spotify are examples of these business models.
Curated Box Subscriptions: Subscribers receive a recurring delivery of products, often tailored to their preferences. These can range from beauty products and fashion items to food and lifestyle goods. This model often capitalizes on the element of surprise and delight, as customers eagerly await their monthly or quarterly deliveries.
Membership Subscriptions: These subscriptions offer access to exclusive communities, perks, and benefits. Fitness clubs, online communities, and professional organizations use this model. These can include discounts, early access to products or services, and a sense of belonging.
Product Subscriptions: Customers receive regular deliveries of physical products they use frequently, such as razors, groceries, or pet supplies. This model focuses on convenience and allows subscribers to automate their replenishment needs. Dollar Shave Club and HelloFresh are examples of this model.
Digital Subscriptions: Providing access to digital content such as streaming services, online games, and e-books. These are a convenient way to provide users with the content they need at a regular price. They are also easy to manage and provide a great deal of flexibility.
Across industries, there are various examples of subscription models, some new, some old, some reinvented. Let's explore some industries that are using this model.
Popular Industries Using Subscription Models
The subscription business model is now present in many different industries. Here is a list of ten industries along with example companies:
- Streaming Services: Netflix, Spotify, Disney+
- Software: Adobe Creative Cloud, Microsoft 365, Salesforce
- News and Media: The New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, The Athletic
- E-commerce: Amazon Prime, Birchbox, Dollar Shave Club
- Education: Coursera, Skillshare, MasterClass
- Health and Wellness: Peloton, Headspace, Calm
- Gaming: Xbox Game Pass, PlayStation Plus, World of Warcraft
- Food and Beverage: Blue Apron, HelloFresh, Graze
- Beauty and Personal Care: Ipsy, FabFitFun, Birchbox
- Business and Productivity: HubSpot, Slack, Zoom
Customers and businesses alike prefer subscription models because they provide a great balance of price versus value. Businesses get a more stable source of income. Customers get the convenience of automatically having the product when they need it, or getting immediate access to new features.
Challenges and Considerations
While subscription models offer significant advantages, they also present certain challenges. One of the primary concerns is customer churn, or the rate at which subscribers cancel their subscriptions. Businesses must work to prevent customer churn by providing ongoing value, adapting to changing consumer needs, and building strong customer relationships. The competition in subscription market can be intense, and businesses have to remain competitive.
Data privacy and security are other critical considerations. Subscription models often require or allow the business to gather substantial amounts of information from the customer (such as magazine mailing lists), and this raises issues of privacy. Businesses must comply with data protection regulations and implement robust security measures to protect customer data.
Pricing and payment models must also be carefully considered. Businesses have to find the right balance between providing value and remaining profitable. Furthermore, they must provide flexible and convenient payment options to cater to the needs of different customer segments.
The Future of Subscriptions
The future of subscriptions looks bright, and there are many opportunities for innovation and growth. We can expect to see further diversification of subscription models, with new offerings emerging across a broader range of industries. Furthermore, we can anticipate the adoption of more sophisticated technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to personalize the user experience and optimize customer engagement. The subscription models operational characteristics make it a reliable revenue source and a method to maintain customer relationships.
Sustainability will also be a significant focus, with businesses seeking to reduce waste, promote the efficient use of resources, and create more ethical and environmentally conscious products and services. As the subscription economy continues to mature, it will be crucial for businesses to adapt to evolving consumer expectations, prioritize customer experience, and continuously innovate. From accessing curated content to leveraging business tools, these models align with evolving consumer demands and technological advancements.
The subscription model represents more than just a business trend. It is a reflection of a fundamental shift in consumer behavior and a testament to the power of access, convenience, and continuous value. Subscription models are poised to continue their transformative journey across the global economy. The key to success lies in providing consistent value, building strong customer relationships, and adapting to an ever-changing landscape. This will lead to sustainable growth and profitability, and further embed the subscription model into the fabric of our daily lives.

![Our guide to subscription business models [2022 Update]](https://www.profitwell.com/hubfs/subscription model-01.jpg#keepProtocol)