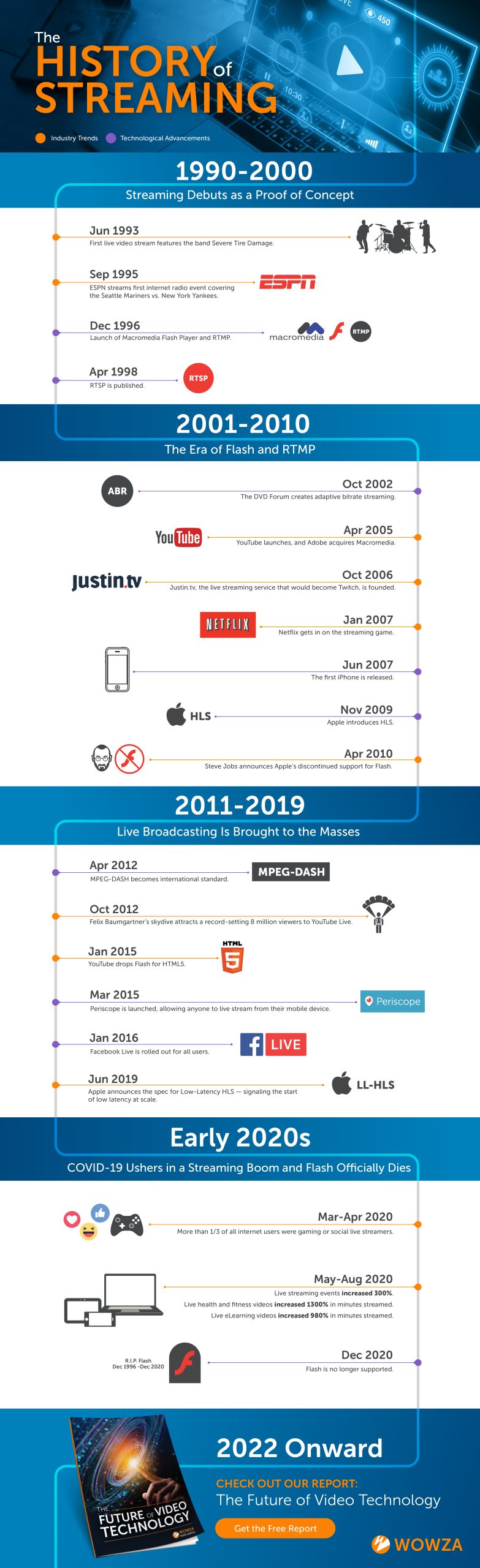
Has the way we consume media been irrevocably transformed? The history of streaming services reveals a dramatic shift in how we access entertainment, offering unprecedented convenience and choice, fundamentally altering the media landscape.
Not so long ago, the phrase "the history of streaming services" would likely have been met with bewilderment. The very concept of instantly accessing video and audio content over the internet was in its infancy. Today, its a ubiquitous part of modern life. Platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video have democratized access to a vast library of content, available at our fingertips, anytime and anywhere. This revolution has fundamentally changed how content is created, distributed, and consumed, and it's a story worth exploring.
The evolution of streaming has been a rapid and multifaceted phenomenon. It's not simply about watching movies and TV shows. It's a technological and cultural shift that has redefined how businesses operate and how individuals interact with the world. To understand the impact, it's useful to break down the elements and track their evolution.
The advent of streaming media, essentially the transfer of multimedia over the internet for immediate consumption by the user, provided the foundation. It's a popular method for conveying and sharing mass media, broken down into data packets that seamlessly transmit content across digital networks. This technology quickly outstripped the previous model of waiting for a scheduled program or purchasing a physical copy.
The initial pioneers of the streaming landscape were not necessarily household names. The early 2000s saw the quiet beginnings of what was to come. Youtube, launching in 2005, provided a platform for user-generated content and acted as an early proving ground for the potential of online video sharing. Then, in 2007, Netflix Inc. launched its streaming service, initially alongside its DVD rental business. This was a seminal moment; the company began the shift toward a digital-first entertainment model that would eventually dominate the industry.
Before these platforms, the options were limited. Cable television, with its bundled channels and scheduled programming, reigned supreme. Radio still offered music, news, and entertainment, but with limited selection and the constraint of live broadcast. The idea of choosing what to watch or listen to, when and where, was a luxury. The "cord-cutting" phenomenon, where individuals and families moved away from traditional cable subscriptions in favor of streaming services, became increasingly common.
Today, the experience has changed fundamentally. The ubiquity of smart devices, high-speed internet, and user-friendly apps have combined to create a seamless, on-demand entertainment experience. Television shows and movies are streamed via apps on devices like Fire Sticks, Roku, and smart TVs. Music streaming services, like Spotify and Apple Music, offer vast catalogs of music at a listener's fingertips. SiriusXM has taken a different route, streaming radio channels over the Internet. The result has been a revolution in consumer habits, impacting everything from entertainment production to marketing strategies.
The streaming revolution continues to evolve. The market is continuously segmented by business models. Subscription models, advertising-supported models, and transactional video-on-demand models create diversity, which allows companies to target various consumers.
James Rothwell, from Comcasts Freewheel, provides insights into how the revolution of streaming led to an evolution of marketing, offering a concise view of how the industry grew. Marketing strategies adapted to the data-driven nature of streaming, allowing for highly targeted advertising and content recommendations, which resulted in a shift from mass marketing to a more personalized approach. These strategies have made streaming platforms more valuable to advertisers and more relevant to the audience.
The story of streaming is not merely about technological advancements. It is a story about shifting consumer behavior and how a cultural shift influences how content is created, distributed, and consumed. The emergence of blockchain technology has added a new layer, with proponents suggesting the ability of blockchain to allow for the encryption and secure storage of video content, offering greater security and control to creators and audiences alike.
The impact of streaming has been widespread, transforming the media landscape and influencing other industries. To understand the full scope of the streaming era, consider the key moments, the pivotal technologies, and the people and companies who drove the change.
To further emphasize the impact of streaming, here is a table containing relevant information about the current landscape of streaming services, their business models, and significant trends.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Growth | The global video streaming market is experiencing substantial growth. Multiple reports estimate the market to be in the hundreds of billions, with further expansion expected in the years to come. |
| Dominant Business Models | Subscription Video on Demand (SVOD) is the most prevalent. Advertising-based Video on Demand (AVOD) is also becoming more common, especially in free or discounted tiers. Transactional Video on Demand (TVOD), where users pay to rent or purchase content, has a niche, but still active, role in the market. |
| Key Players | Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Hulu are the leading platforms. Numerous other services cater to specific niches, such as HBO Max (now Max), Paramount+, and others. |
| Content Trends | Original content, diverse programming, and international content are crucial trends. Platforms are investing heavily in original series and movies, and expanding into new genres. Increased investment in content from different regions of the world is another significant trend. |
| Technological Advancements | 4K and HDR (High Dynamic Range) video quality are standard. Emerging technologies include immersive audio formats, improvements in recommendation algorithms, and the use of artificial intelligence in content creation and curation. |
| Impact on Traditional Media | Streaming services have disrupted the traditional cable television model and changed how people consume movies and TV shows. Many people are choosing to cut the cord, subscribing to streaming services instead of traditional cable or satellite services. |
| Consumer Behavior | Consumers demand convenience and on-demand access. Binge-watching is a common behavior, and viewers increasingly expect content to be available on a wide range of devices. The ability to watch content anywhere, anytime, is a significant factor. |
| Monetization Strategies | The subscription-based revenue is the main business model. Some platforms have included advertising for revenue diversification and/or lower subscription costs. |
| Future Outlook | The future of streaming includes continued growth of original content, consolidation of streaming services, and greater personalization. Further innovation in streaming technology is likely. |
The streaming services market is complex, but the shift toward on-demand media consumption is undeniable. The landscape is shaped by technological advancements, business models, and consumer preferences. A great way to learn more about the subject is to search for the latest developments on websites such as the IAB and Statista, or to review the annual reports of publicly traded companies, which give the most up-to-date and comprehensive information about trends. The story of streaming is one of continuous evolution, and the future promises more transformative changes in how we enjoy media.